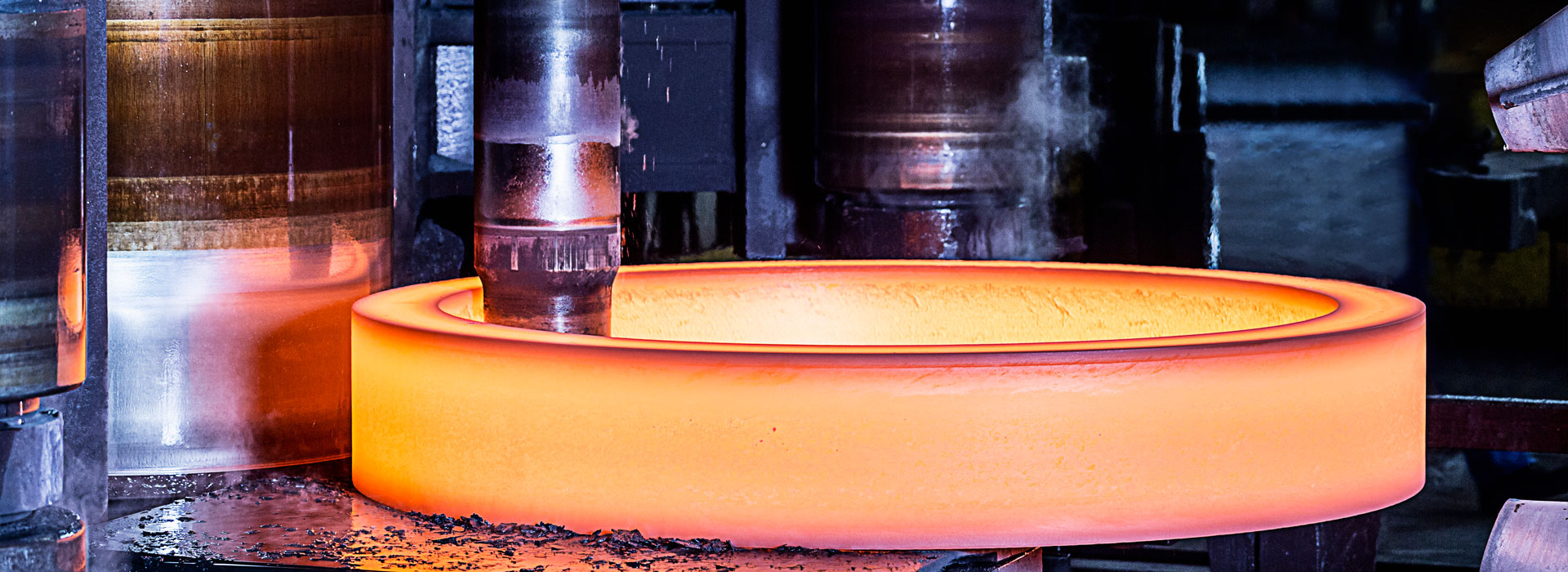
Spray quenching process for forging
2022-07-19
The final heat treatment of forgings requiring higher hardness is mainly applied spray quenching.
Heating, can use ordinary heat treatment furnace through burning heating, according to the diameter of the roll body to determine the holding time, so that part of the spherical secondary carbide decomposition, solution to austenite and homogenization. Differential temperature rapid heating process has been used. Differential temperature heating is beneficial to reduce the quenching stress, but it keeps the core strength of the roll at the level of annealing strength and the production efficiency of single heating is low. It is not suitable for this kind of hot roll with deep pass.
Spray quenching of forgings does not really belong to quenching in the strict sense, because the phase transformation is still pearlite shape transformation, but accelerated cooling to refine the pearlite structure, get cable body, and the final structure is cable body + block eutectic carbide + granular secondary carbide. This increases strength, hardness and wear resistance.
Based on this process idea, the quenching process is divided into spray cooling stage and spray cooling stage. In the first stage of spray cooling, the roller temperature is very high, and a strong spray mist is selected for rapid cooling, and the temperature of the surface layer of the roller is rapidly reduced to the appropriate temperature, in order to inhibit the precipitation of proeutectoid carbide, so as to prevent the emergence of network carbide. In the second stage of cooling, the cooling intensity can be slowed down by spraying air to reduce the quenching stress and gradually transfer heat from the core. When the roller surface is cooled to 450-550℃, the surface of the roll has been completely transformed, and the spraying cooling can be stopped and tempering can be carried out.
In the tempering stage, the temperature should be maintained at 400-500℃ first, and the core should be heated to 550-650℃ after the full transformation, so as to reduce the quenching stress and adjust the hardness of the roll surface to meet the technical requirements.
Heating, can use ordinary heat treatment furnace through burning heating, according to the diameter of the roll body to determine the holding time, so that part of the spherical secondary carbide decomposition, solution to austenite and homogenization. Differential temperature rapid heating process has been used. Differential temperature heating is beneficial to reduce the quenching stress, but it keeps the core strength of the roll at the level of annealing strength and the production efficiency of single heating is low. It is not suitable for this kind of hot roll with deep pass.
Spray quenching of forgings does not really belong to quenching in the strict sense, because the phase transformation is still pearlite shape transformation, but accelerated cooling to refine the pearlite structure, get cable body, and the final structure is cable body + block eutectic carbide + granular secondary carbide. This increases strength, hardness and wear resistance.
Based on this process idea, the quenching process is divided into spray cooling stage and spray cooling stage. In the first stage of spray cooling, the roller temperature is very high, and a strong spray mist is selected for rapid cooling, and the temperature of the surface layer of the roller is rapidly reduced to the appropriate temperature, in order to inhibit the precipitation of proeutectoid carbide, so as to prevent the emergence of network carbide. In the second stage of cooling, the cooling intensity can be slowed down by spraying air to reduce the quenching stress and gradually transfer heat from the core. When the roller surface is cooled to 450-550℃, the surface of the roll has been completely transformed, and the spraying cooling can be stopped and tempering can be carried out.
In the tempering stage, the temperature should be maintained at 400-500℃ first, and the core should be heated to 550-650℃ after the full transformation, so as to reduce the quenching stress and adjust the hardness of the roll surface to meet the technical requirements.
According to the provisions of the standard, the minimum tempering temperature of steel is 675℃, taking into account the impact of tempering parameters on the mechanical properties of forgings, it is necessary to put the tempering after quenching together with the effect of hydrogen elimination and post-welding stress elimination annealing, determine the temperature and time used in each stage.

Previous:Wheel forging
X
We use cookies to offer you a better browsing experience, analyze site traffic and personalize content. By using this site, you agree to our use of cookies.
Privacy Policy