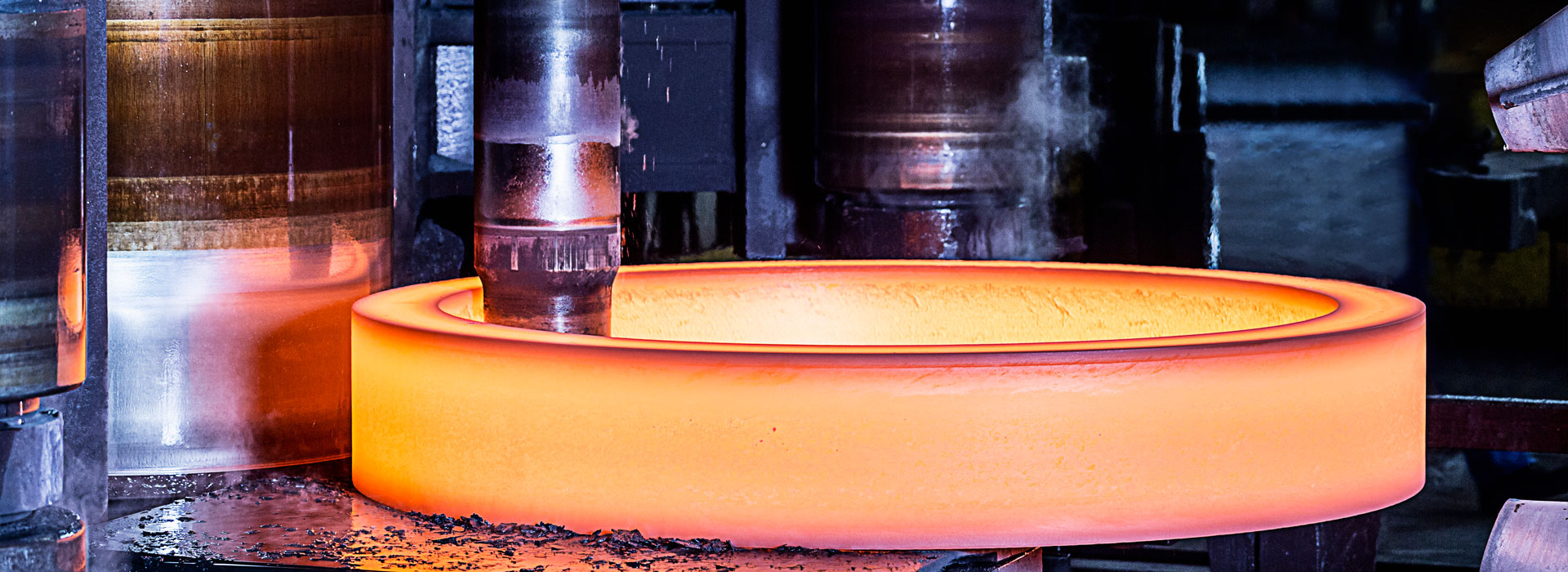
What is Special forging
2022-08-23
The process of melting the metal into a liquid that meets certain requirements and pouring it into the casting mold. After cooling solidification and cleaning treatment, the casting (parts or blanks) with predetermined shape, size and performance are obtained. The basic technology of modern machinery manufacturing industry. The cost of casting blank is low, for the parts with complex shape, especially with complex cavity, it can show its economy. At the same time, it has a wide adaptability, and has better comprehensive mechanical properties. However, the materials (such as metal, wood, fuel, molding materials, etc.) and equipment (such as metallurgical furnace, sand mixing machine, molding machine, core making machine, sand falling machine, shot blasting machine, etc.) required by casting production are more, and will produce dust, harmful gas and noise and pollute the environment.
Casting is a kind of metal hot working technology mastered earlier by human, which has a history of about 6000 years. In 3200 BC, copper frog castings appeared in Mesopotamia. From the 13th century BC to the 10th century BC, China had entered the heyday of bronze castings, and the technology had reached a very high level. For example, Simuwu square tripod weighing 875 kg in the Shang Dynasty, Zeng Marquis Yi Zun plate in the Warring States Period and light shining mirror in the Western Han Dynasty were all representative products of ancient casting. Early casting was greatly influenced by pottery, and most castings were tools or utensils for agricultural production, religion, life and other aspects, with strong artistic color. In 513 BC, the earliest written piece of cast iron in the world, the Jin Ding (about 270 kg), was cast in China. Around the 8th century, cast iron began to be produced in Europe. After the industrial revolution in the 18th century, castings entered a new period of service for big industry. In the 20th century, casting developed rapidly. Ductile iron, malleable cast iron, ultra-low carbon stainless steel, aluminum copper, aluminum silicon, aluminum magnesium alloy, titanium base, nickel base alloy and other casting metal materials have been developed, and a new technology for the inoculation of gray cast iron has been invented. After 1950s, there appeared high pressure molding of wet sand, chemical hardening sand molding, core-making, negative pressure molding and other special casting, shot blasting cleaning and other new processes.
There are many kinds of casting, according to the modeling method, it is customary to divide into: ① ordinary sand casting, including wet sand, dry sand and chemical hardening sand. (2) special casting, press molding materials and can be divided into natural mineral sand as the main special casting molding materials (e.g., investment casting, mold casting, shell mold casting foundry, negative pressure casting, mold casting, ceramic mold casting, etc.) and metal as the main mold material of special casting (such as metal mold casting, pressure casting, continuous casting, low pressure casting, centrifugal casting, etc.). Casting process usually includes: (1) cast (containers) makes liquid metal solid casting, casting according to the materials can be divided into sand mold, metal, ceramic, mud, graphite, etc., can be divided by use disposable, semi permanent and permanent type, mold preparation quality are the main factors influencing the casting quality; ② The melting and pouring of casting metal, casting metal (casting alloy) mainly includes cast iron, cast steel and cast non-ferrous alloy; (3) Casting treatment and inspection, casting treatment including removal of core and casting surface foreign bodies, removal of pouring riser, shovel burr and seam protrusion, heat treatment, shaping, rust treatment and rough machining.

Casting is a kind of metal hot working technology mastered earlier by human, which has a history of about 6000 years. In 3200 BC, copper frog castings appeared in Mesopotamia. From the 13th century BC to the 10th century BC, China had entered the heyday of bronze castings, and the technology had reached a very high level. For example, Simuwu square tripod weighing 875 kg in the Shang Dynasty, Zeng Marquis Yi Zun plate in the Warring States Period and light shining mirror in the Western Han Dynasty were all representative products of ancient casting. Early casting was greatly influenced by pottery, and most castings were tools or utensils for agricultural production, religion, life and other aspects, with strong artistic color. In 513 BC, the earliest written piece of cast iron in the world, the Jin Ding (about 270 kg), was cast in China. Around the 8th century, cast iron began to be produced in Europe. After the industrial revolution in the 18th century, castings entered a new period of service for big industry. In the 20th century, casting developed rapidly. Ductile iron, malleable cast iron, ultra-low carbon stainless steel, aluminum copper, aluminum silicon, aluminum magnesium alloy, titanium base, nickel base alloy and other casting metal materials have been developed, and a new technology for the inoculation of gray cast iron has been invented. After 1950s, there appeared high pressure molding of wet sand, chemical hardening sand molding, core-making, negative pressure molding and other special casting, shot blasting cleaning and other new processes.
There are many kinds of casting, according to the modeling method, it is customary to divide into: ① ordinary sand casting, including wet sand, dry sand and chemical hardening sand. (2) special casting, press molding materials and can be divided into natural mineral sand as the main special casting molding materials (e.g., investment casting, mold casting, shell mold casting foundry, negative pressure casting, mold casting, ceramic mold casting, etc.) and metal as the main mold material of special casting (such as metal mold casting, pressure casting, continuous casting, low pressure casting, centrifugal casting, etc.). Casting process usually includes: (1) cast (containers) makes liquid metal solid casting, casting according to the materials can be divided into sand mold, metal, ceramic, mud, graphite, etc., can be divided by use disposable, semi permanent and permanent type, mold preparation quality are the main factors influencing the casting quality; ② The melting and pouring of casting metal, casting metal (casting alloy) mainly includes cast iron, cast steel and cast non-ferrous alloy; (3) Casting treatment and inspection, casting treatment including removal of core and casting surface foreign bodies, removal of pouring riser, shovel burr and seam protrusion, heat treatment, shaping, rust treatment and rough machining.

Previous:Main classification of forging
X
We use cookies to offer you a better browsing experience, analyze site traffic and personalize content. By using this site, you agree to our use of cookies.
Privacy Policy