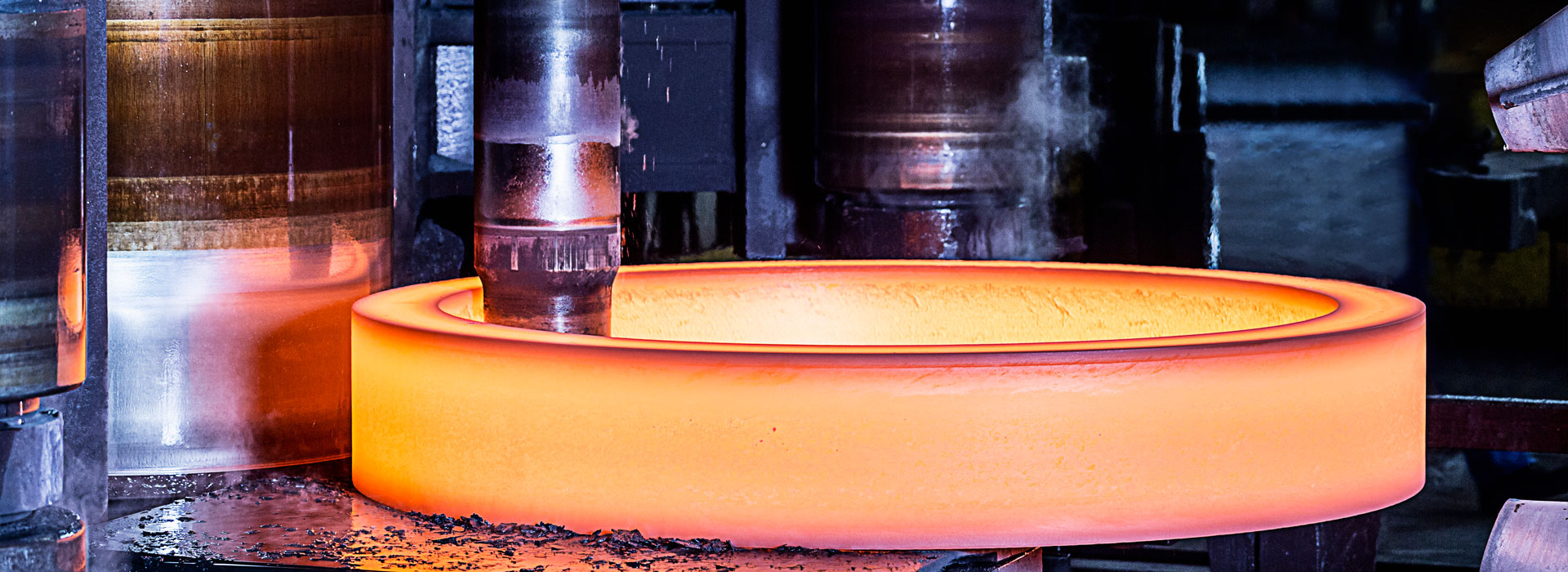
What kinds of forging heat treatment heating can be divided into?
2022-05-24
According to the provisions of the standard, the minimum tempering temperature of steel is 675℃, taking into account the impact of tempering parameters on the mechanical properties of forgings, it is necessary to put the tempering after quenching together with the effect of hydrogen elimination and post-welding stress elimination annealing, determine the temperature and time used in each stage.
When the steel is required to be annealed at 690℃ for up to 24h after welding, in order to still ensure that the mechanical properties of the base metal will not be reduced, the tempering temperature after quenching should be selected lower, generally at 650℃. The annealing of steel after welding is required to be carried out at the lower temperature of 610℃, and the best tempering parameter is about 19, so after quenching, the best tempering temperature for mechanical properties can be obtained directly at 650℃.
The calculation of tempering parameters has been reported in many literatures. At this point, the tempering temperature and time in different periods such as quenching, welding intermediate annealing and post-welding annealing should be converted to the tempering under different equivalent holding time at the same temperature, and then calculate the tempering parameters according to the sum of the temperature and equivalent time.
Forgings heat treatment heating, according to the furnace temperature of forgings into the furnace can be divided into three cases.
Cold forgings into the furnace temperature has risen to quenching or normalizing temperature of the furnace heating, which is the most commonly used for small parts of a heating method, but for large forgings is a rapid heating range, with the improvement of the metallurgical quality of forgings, this heating method in the application of large forgings is more and more.
The cold forgings are put into the furnace with the heating up of the furnace, and are kept for a period of time before reaching the phase transition point, and then continue to be heated to the required temperature. This is the most common way of heating forgings, in the heat treatment of small parts is rarely used, generally called ladder heating.
When the steel is required to be annealed at 690℃ for up to 24h after welding, in order to still ensure that the mechanical properties of the base metal will not be reduced, the tempering temperature after quenching should be selected lower, generally at 650℃. The annealing of steel after welding is required to be carried out at the lower temperature of 610℃, and the best tempering parameter is about 19, so after quenching, the best tempering temperature for mechanical properties can be obtained directly at 650℃.
The calculation of tempering parameters has been reported in many literatures. At this point, the tempering temperature and time in different periods such as quenching, welding intermediate annealing and post-welding annealing should be converted to the tempering under different equivalent holding time at the same temperature, and then calculate the tempering parameters according to the sum of the temperature and equivalent time.
Forgings heat treatment heating, according to the furnace temperature of forgings into the furnace can be divided into three cases.
Cold forgings into the furnace temperature has risen to quenching or normalizing temperature of the furnace heating, which is the most commonly used for small parts of a heating method, but for large forgings is a rapid heating range, with the improvement of the metallurgical quality of forgings, this heating method in the application of large forgings is more and more.
The cold forgings are put into the furnace with the heating up of the furnace, and are kept for a period of time before reaching the phase transition point, and then continue to be heated to the required temperature. This is the most common way of heating forgings, in the heat treatment of small parts is rarely used, generally called ladder heating.
Cold forgings are heated in a furnace whose temperature has risen to 100-120℃ higher than the temperature of quenching or normalizing. Whether for small parts or large forgings are fast heating, but in the heat treatment of large forgings heating is rarely used, only in special occasions, such as cold rolling differential temperature and heat treatment is also used in this heating way.



X
We use cookies to offer you a better browsing experience, analyze site traffic and personalize content. By using this site, you agree to our use of cookies.
Privacy Policy